The Three Leopards
on Mar 12, 2024The origin of the word “Leopard” traces back to the early 13th Century from Old French where they used the word Lebard or Leupart as a surname. This surname meant “A large cat of the wooded country of Africa and Asia”. This evolved then to late Latin leopardus that literally means “Lion-pard, lion-panther”. The leopard was believed to be a hybrid animal between the lion and panther, hence the combination of the two names. Afterwards the Greek word leopardus formed from leon (lion) and pardus (male panther).
In today’s Taxonomy the leopard is named Panthera pardus. Leopards belong to the big cat genus Panthera, where the rest of the taxonomic name comes from the Greek word leopardus where pardus means panther.
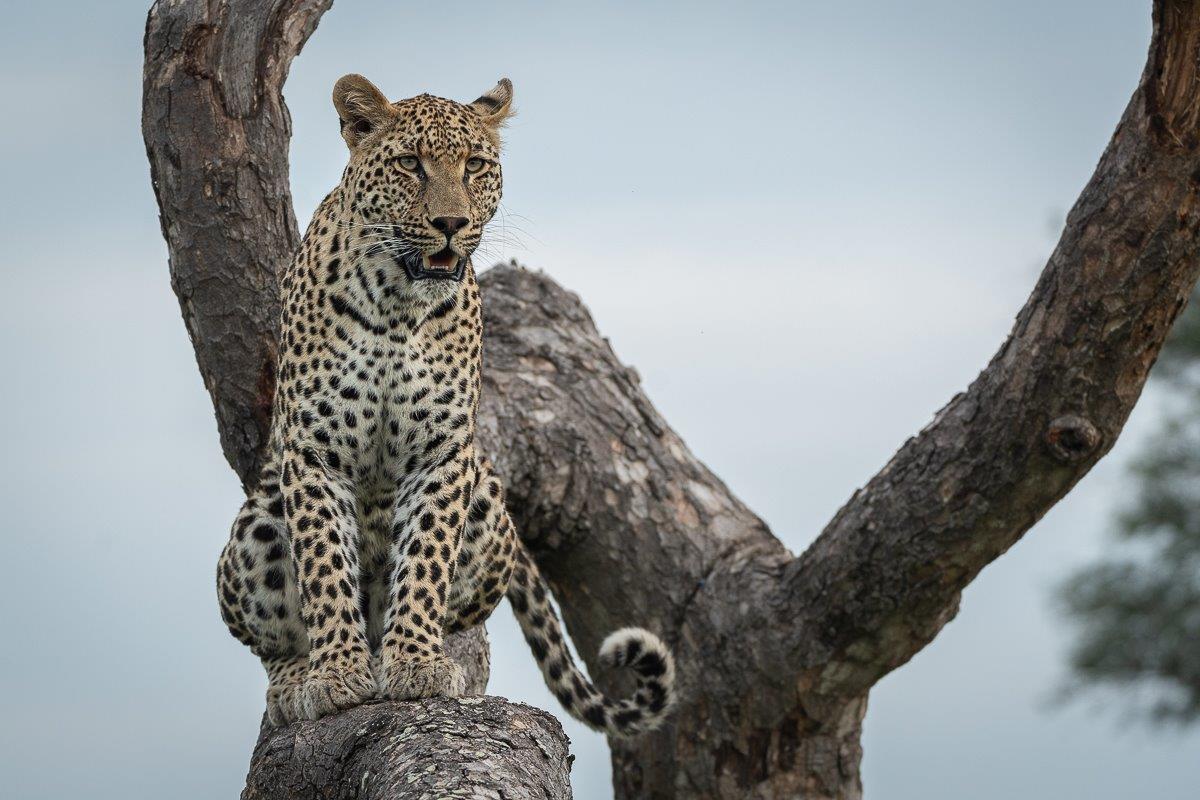

There are 9 different subspecies of leopards, which can be distinguished by the characteristics of their coat, but it is not just the mammal leopard that has this pattern. All throughout the Plantae and Animalia Kingdom you can find this unique set of spots.
African Leopard
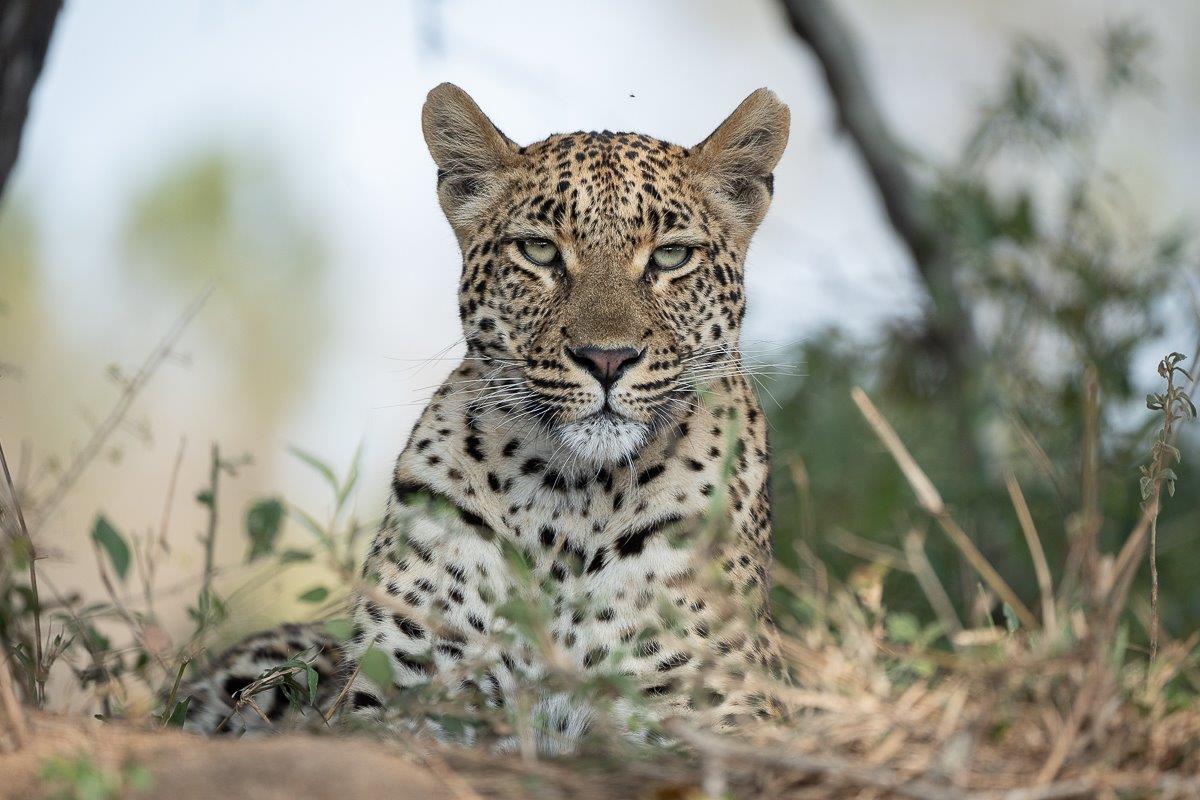
Sabi Sabi is well known for incredible leopard sightings but what is it about these elusive animals that makes them so unique?
Characterised by their striking rosette pattern, they possess a remarkable ability to blend into their surroundings seamlessly, making them elusive and formidable hunters. They have keen senses, including acute vision and hearing, enabling them to navigate through diverse terrains and make them excellent trackers.
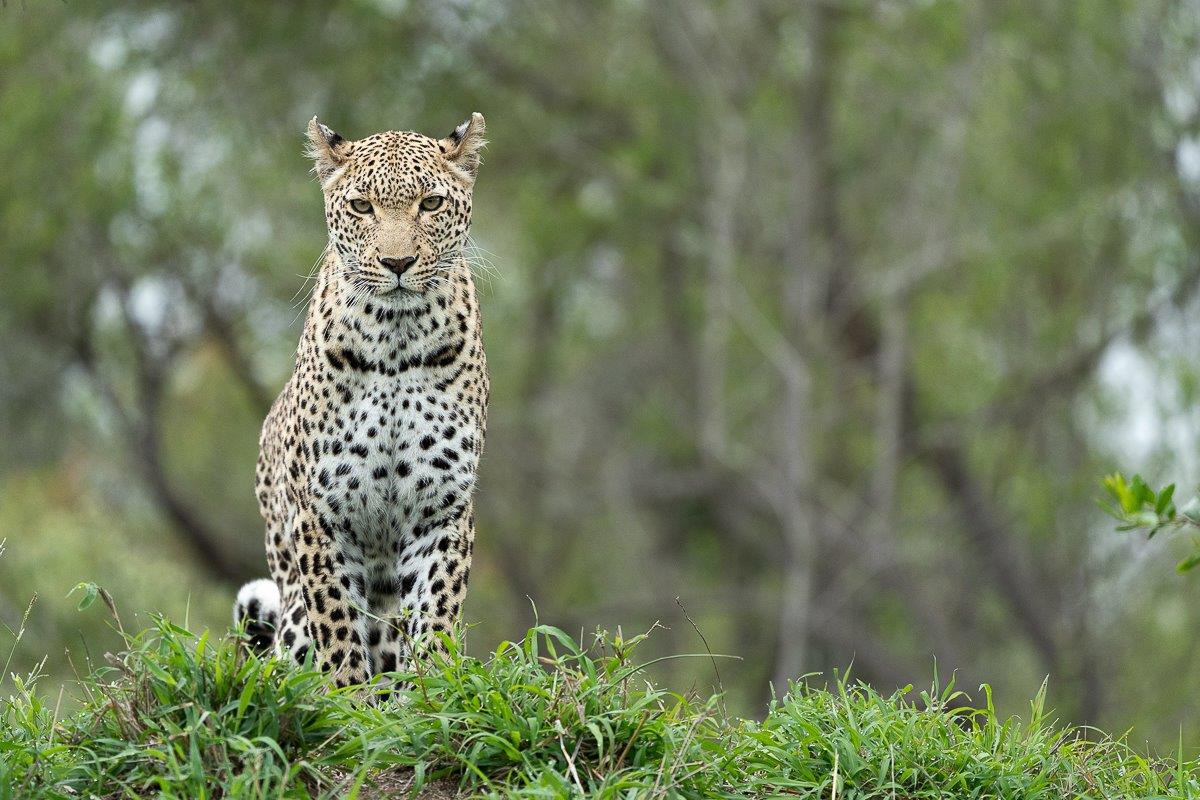

While many big cats, such as lions, form social groups or prides, leopards are solitary animals, preferring to roam and hunt alone. But this is not to say that you will never see more than one leopard together. Cubs are dependent on their mothers for the first year to year and a half of their life. They rely on her to feed and protect them in their most vulnerable stages of their life. She will hide them away at a den site while she goes hunting, and after securing a meal up in a tree, she will fetch and take them to the kill. Cubs learn how to climb trees at a very young age, enabling them to run/hide away from predators when mom is not around.
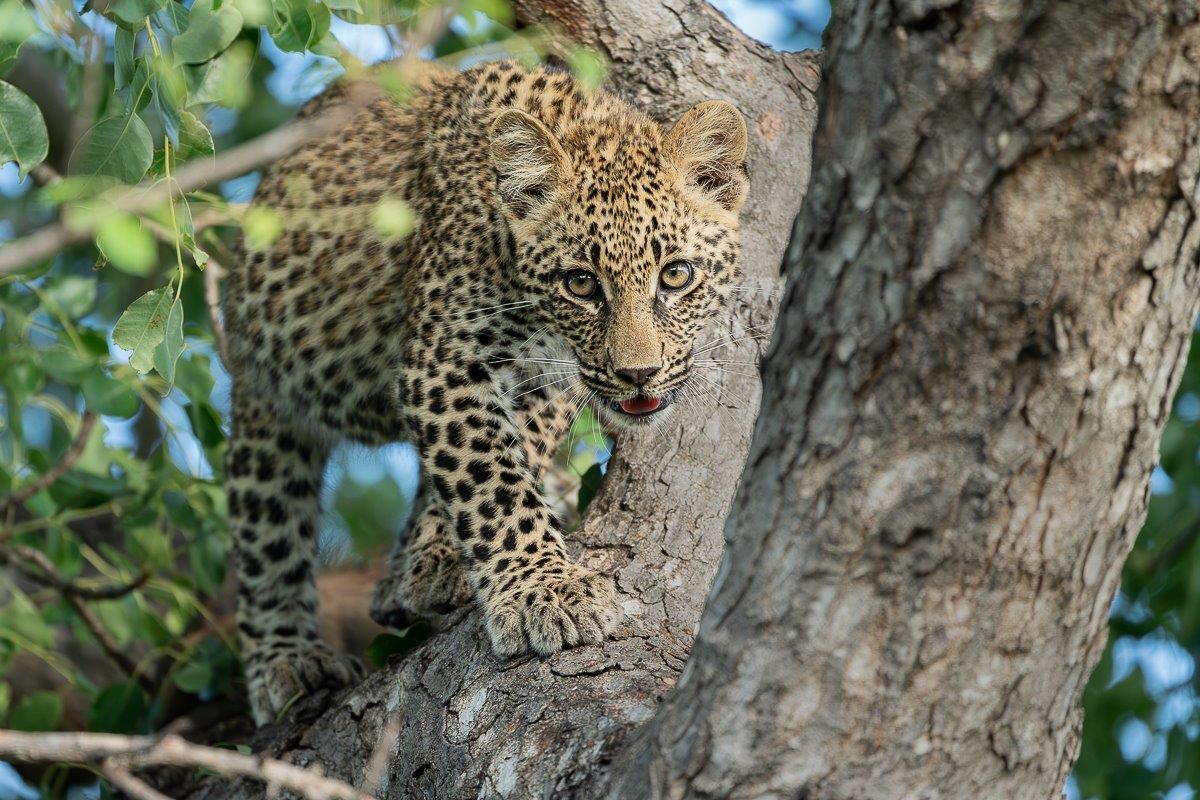

Renowned for their ability to climb trees with ease, they often hoist their kills onto branches to keep it safe from scavengers such as hyenas and lions. This arboreal prowess sets leopards apart from the other big cats and underscores their ability to adapt to a variety of environments, ranging from dense forests to open savannas.
Leopards are known for their resourcefulness to thrive even in a human-dominated landscape. Despite facing numerous threats such as deforestation, habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflict, leopards demonstrate a remarkable resilience and adaptability, finding ways to coexist.

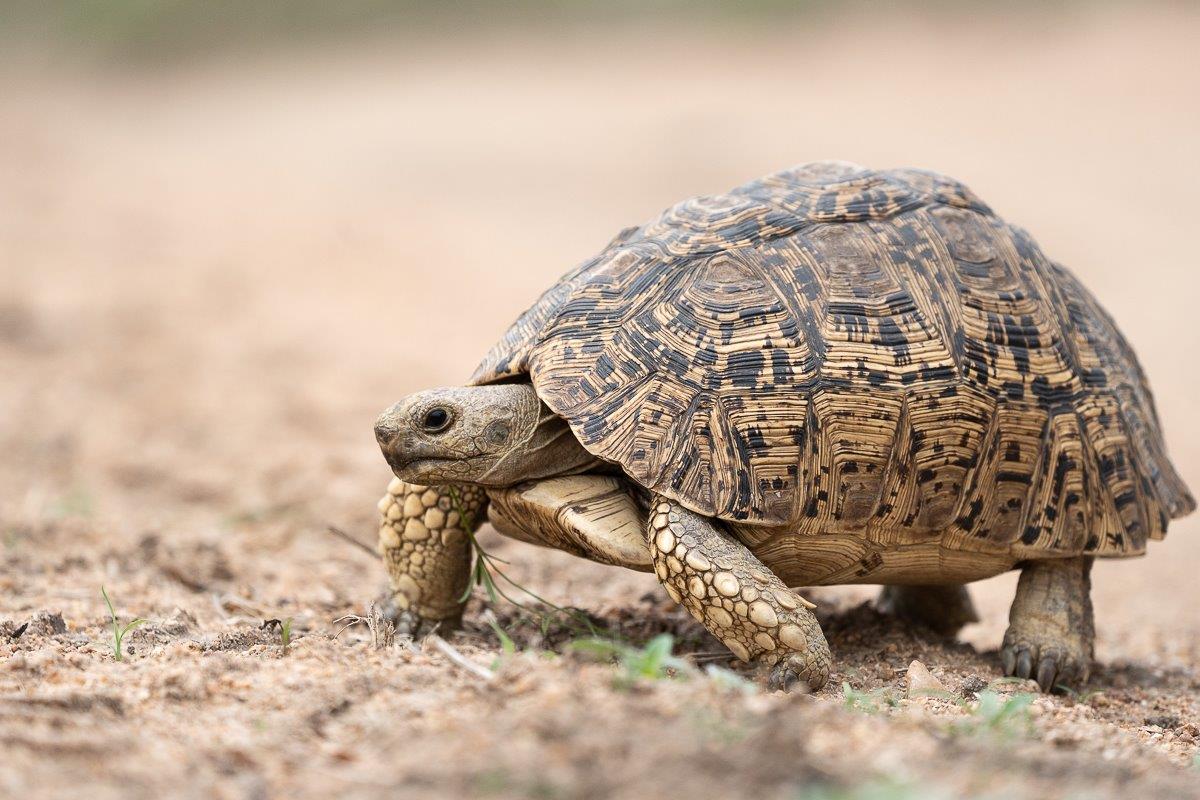
Leopard Tortoise
The Leopard tortoise (Stigmochelys pardalis) is the fourth largest tortoise in the world. Their scientific name is a combination of the Greek words Stigma (marked) and chelone (tortoise), were as pardalis is derived from the Greek word that means spotted. Living up to their Greek and English names, this tortoise has the beautiful pattern of yellow, tan and brown rings that they have on their shell that resembles that of the rosette pattern of a leopard.
Not to be confused by a turtle and a terrapin, the Leopard tortoise is the only tortoise in the family that can swim, this is due to not having a nuchal shield. This is a shield that protects the scute above the neck. By not having this shield, it means that they can raise their head, especially when they are in water. Their large domed shell also helps them with their buoyancy when they are in water. Being crepuscular, they are active during early mornings and just before the sun sets. During the most part of the day they try to seek shade and avoid being active at the hottest part of the day.

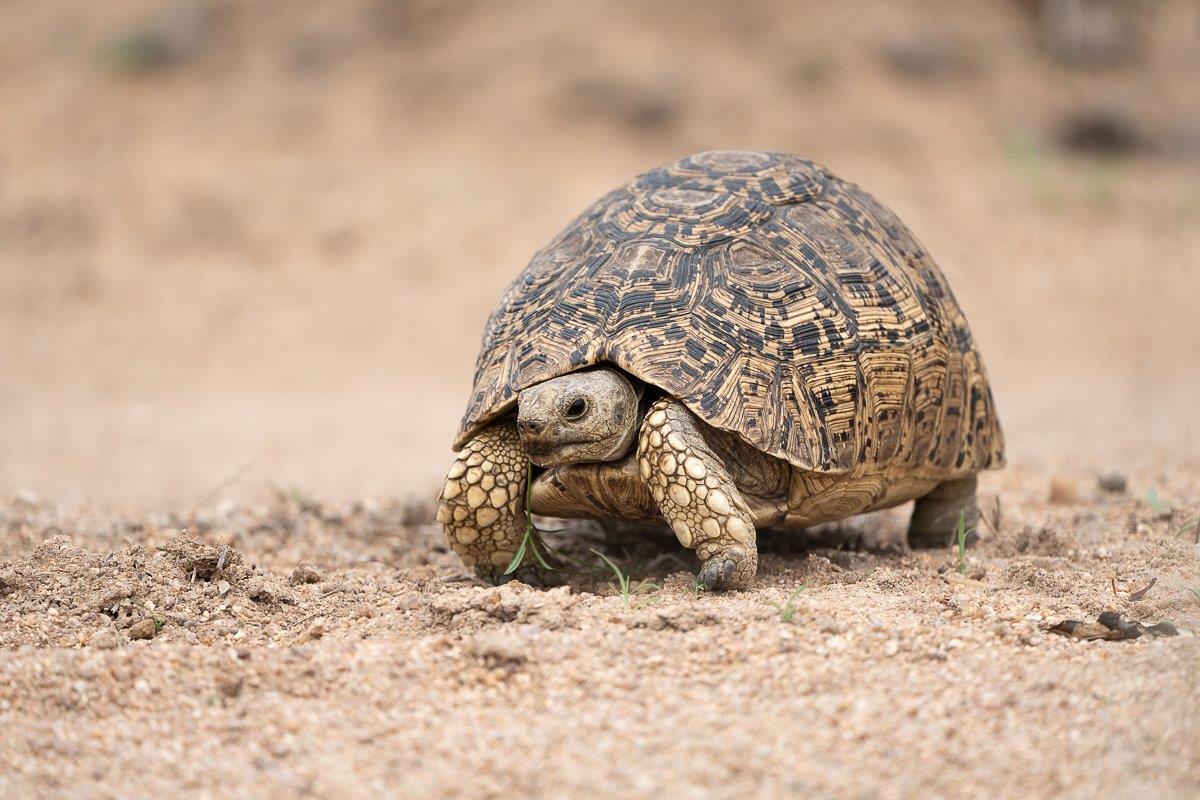
Eating plant matter most of the time, it is known that the Leopard tortoise will also feed on hyena droppings (coprophagia) and chew on animal bones (osteophagia). Both the droppings and the bones are high in minerals that help the tortoise to keep a strong and healthy shell and also helps females in producing eggshells.
Panels on the shell of the tortoise are called “scutes”. The scutes will grow in conjunction with the growing seasons, helping us to age a tortoise. Similar to counting the rings on a tree, one can count the ridges on the shell.
During the dry winter months, they can store water in what is called a “bursa sac”. This reserve water is used for hydration as well as to moisten the soil when the female is ready to dig a nest to lay her eggs. When stressed, they release the water that is stored in the bursa sac as a defence mechanism. This is why we should not pick up a tortoise during winter, and even summer, as they lose this reserve water and might not be able to refill their bursa sac in time again. We do not see them as often during the winter months as they will shelter in holes in the ground, or under rocks and logs, where they dig themselves in or under, with only the shell being visible.

Leopard Orchid
The Leopard orchid (Ansellia Africana) is a species endemic to Africa. Discovered by John Ansell in West Africa in the nineteenth century, he took the first specimen back to Europe, hence the scientific name Ansellia. With brown spots on their yellow flower petals, this resembles the spots of a leopard’s coat, giving them the English name, the Leopard Orchid.
Making its home in the branches of trees, they are known as an epiphyte, feeding off dead leaves and other debris, without harming the tree, they use the structure of the tree in order to get maximum sunlight. Thin aerial roots form a basket shape that are used to catch any falling leaves from the tree, this basket is sometimes referred to as the “trash basket”. The dead leaves are then broken down by fungi that live together with the orchid, and then absorbed by the roots of the orchid.
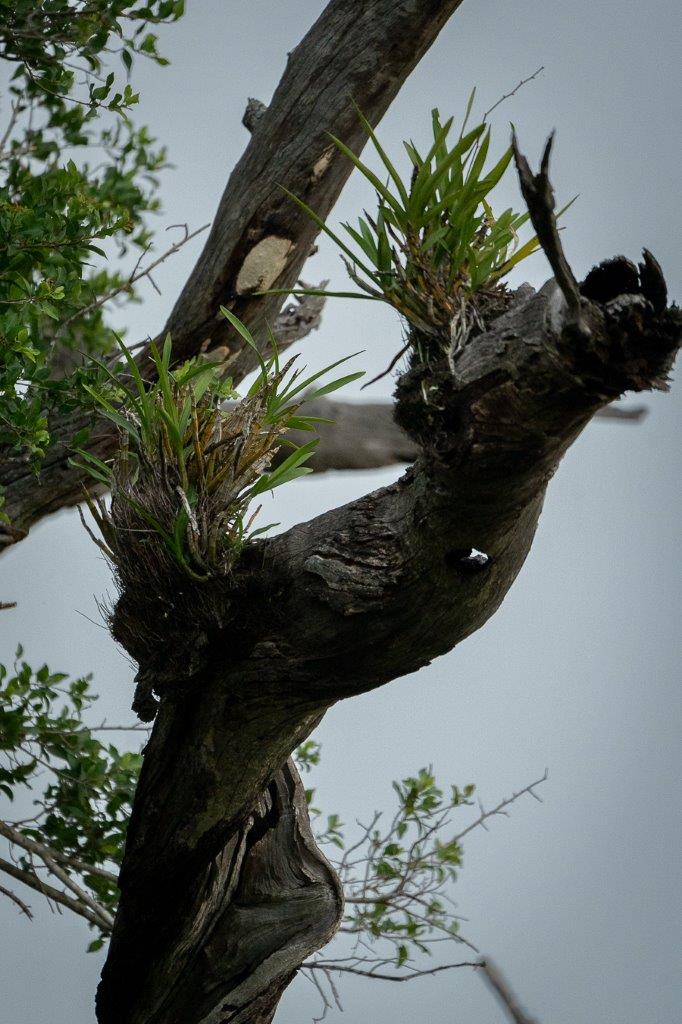

The Leopard Orchid is recognisable by the long stems that have yellow spindle-shaped swellings called pseudobulbs, growing up to 60cm long. Six or seven leaves grow on alternating sides of the top of the pseudobulb. Flowering stems growing from the top of the pseudobulbs, can hold up to 100 flowers each when they flower in spring and summer.
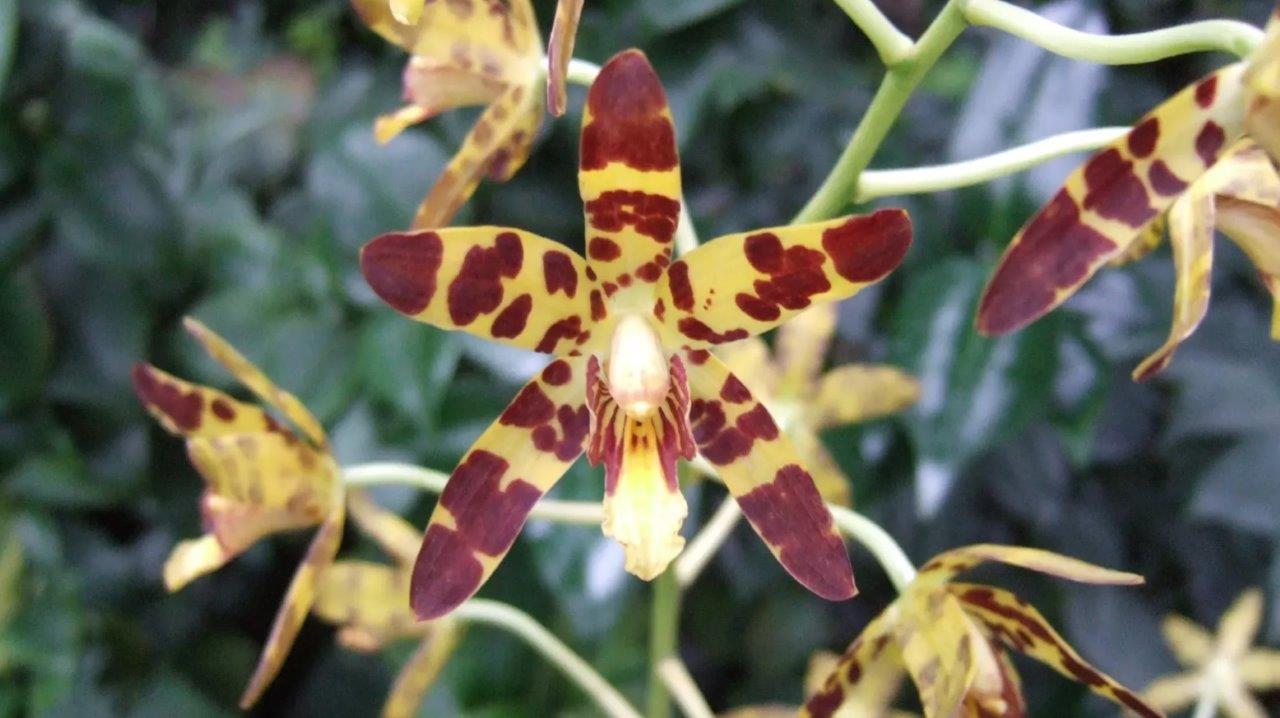

Attracting different species, the Leopard Orchid is important for the survival of a few different species. At nighttime, insects like Hawk Moths will feed on the sweet nectar within the flower. A few different bird species will also use the basket that is being created as a nest, well hidden from the outside world.
With a few traditional beliefs, this is considered to be an important plant in the local communities. In some traditions it is used as a love charm and is believed that if you climb up a tree, pick the roots of the Leopard Orchid, chew on it and spit it out while saying their desired partners name, the person that they are admiring will think of them. It has been documented in various traditional medicine studies that it can be used for madness as well, as it has effects on the central nerves system. In Western medicine, studies have shown that this orchid can be used as a treatment for Alzheimer's disease as it has many sources of biomolecules.
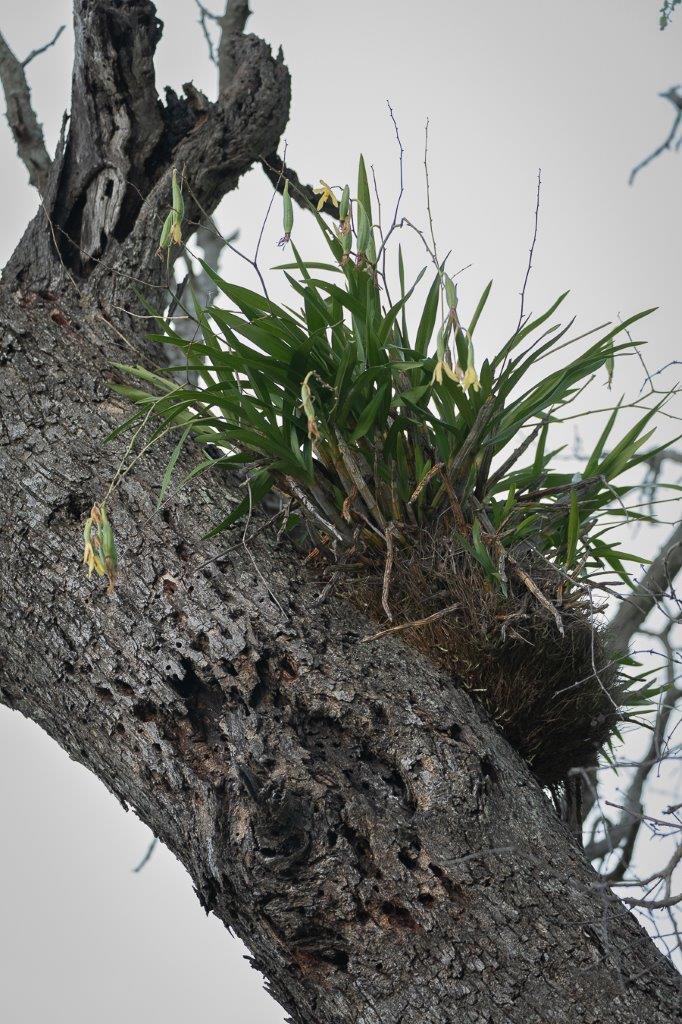

Next time when you are out on safari, remember to look out for the lesser known “Leopards” camouflaged in the bush.
Blog by Daniel Greyvenstein (Bush Lodge Ranger)